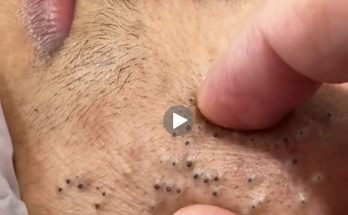
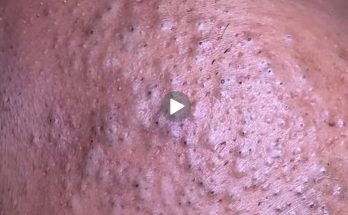
Fatty lumps under the skin are a common concern and are usually harmless, but they can cause discomfort or cosmetic worry for many people. These soft, movable lumps are often known as lipomas, which are slow-growing growths made of fatty tissue. They can appear on the arms, shoulders, back, neck, thighs, or abdomen and are generally painless. Although most fatty lumps do not require medical treatment, understanding their causes and available treatment options can help you manage them safely and effectively.
The exact cause of fatty lumps is not always clear, but several factors may contribute to their development. Genetics plays a major role, as lipomas tend to run in families. Hormonal changes, minor injuries, or metabolic conditions may also trigger their formation. In most cases, these lumps grow slowly over time and remain benign. However, any lump that becomes painful, hard, rapidly growing, or changes in appearance should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out other conditions.
For many people, observation is the first and simplest approach. If the fatty lump is small, painless, and not causing any functional problems, doctors often recommend leaving it alone. Regularly monitoring the size and texture of the lump can help identify any changes early. Avoid pressing or massaging the lump aggressively, as this will not make it disappear and may cause irritation.
When treatment is desired, medical procedures are the most effective and reliable options. Surgical removal is a common and permanent solution, especially if the lump is large, uncomfortable, or cosmetically concerning. This minor procedure is usually done under local anesthesia and involves removing the entire fatty growth, which reduces the chance of recurrence. Another option is liposuction, which may be used for larger lipomas and leaves smaller scars, although it may not remove the entire capsule.
In some cases, non-surgical treatments may be considered. Steroid injections can help shrink certain fatty lumps by reducing inflammation and fat accumulation, though they rarely eliminate the lump completely. These treatments are typically recommended only after proper medical evaluation.
While there is limited scientific evidence supporting home remedies, maintaining a healthy lifestyle may help prevent new fatty lumps from forming. Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, managing body weight, and staying hydrated support overall skin and tissue health. Some people use warm compresses to ease mild discomfort, but this will not remove the lump itself.
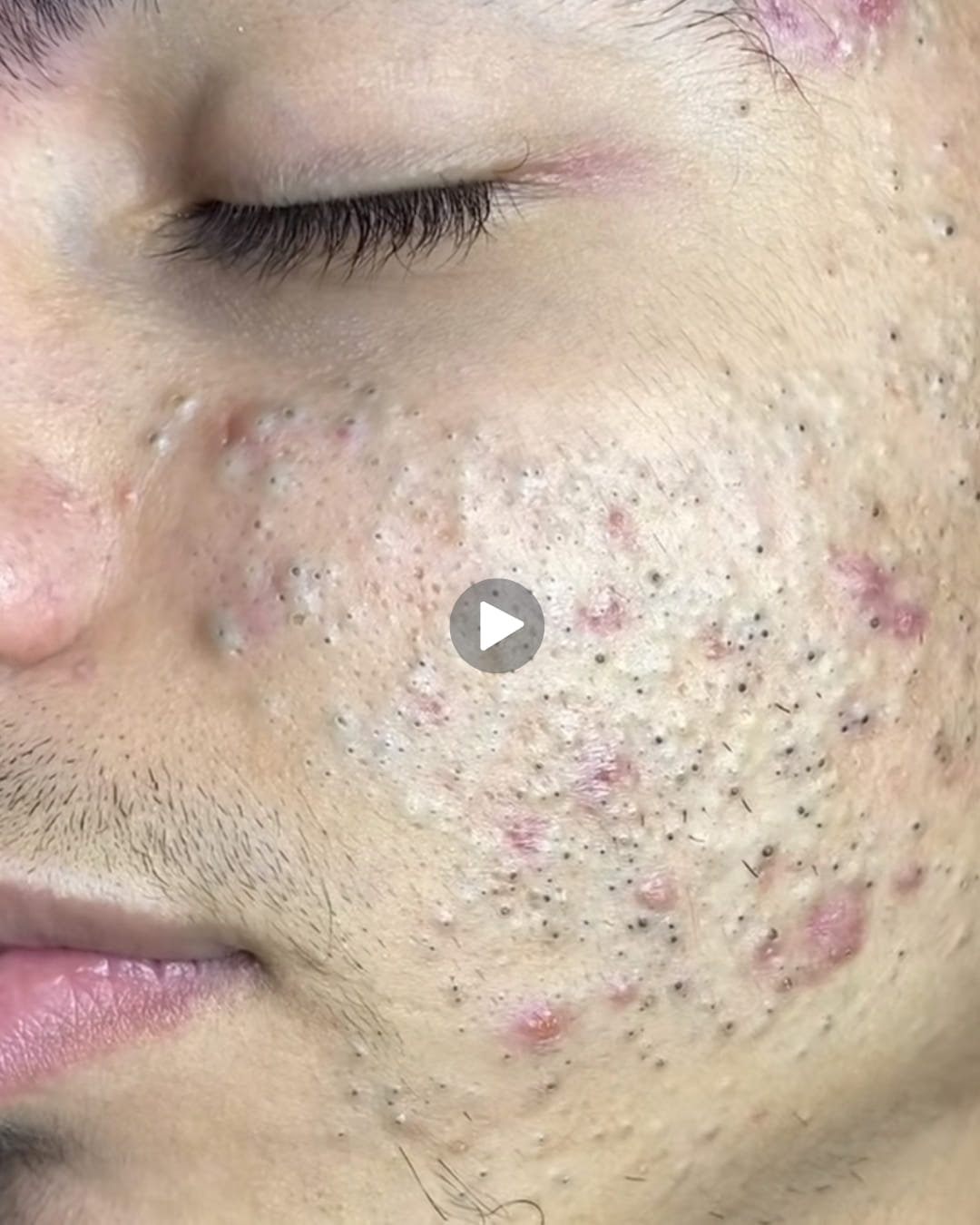
It is important to avoid attempting to pop, squeeze, or cut fatty lumps at home. Doing so can lead to infection, scarring, and serious complications. Self-treatment without medical guidance is unsafe and ineffective.
If you notice multiple fatty lumps, rapid growth, or pain, consulting a dermatologist or surgeon is essential. Early evaluation ensures proper diagnosis and helps determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
With the right medical advice and treatment approach, fatty lumps under the skin can be managed safely, restoring comfort and peace of mind.